The most dangerous symptom of an allergic reaction is your body going into anaphylaxis. It creates a significant problem within the immune system and contributes to poor blood circulation and heart issues.
If you are at risk from allergies and are concerned about your blood circulation, here’s all you need to know about how they work together.
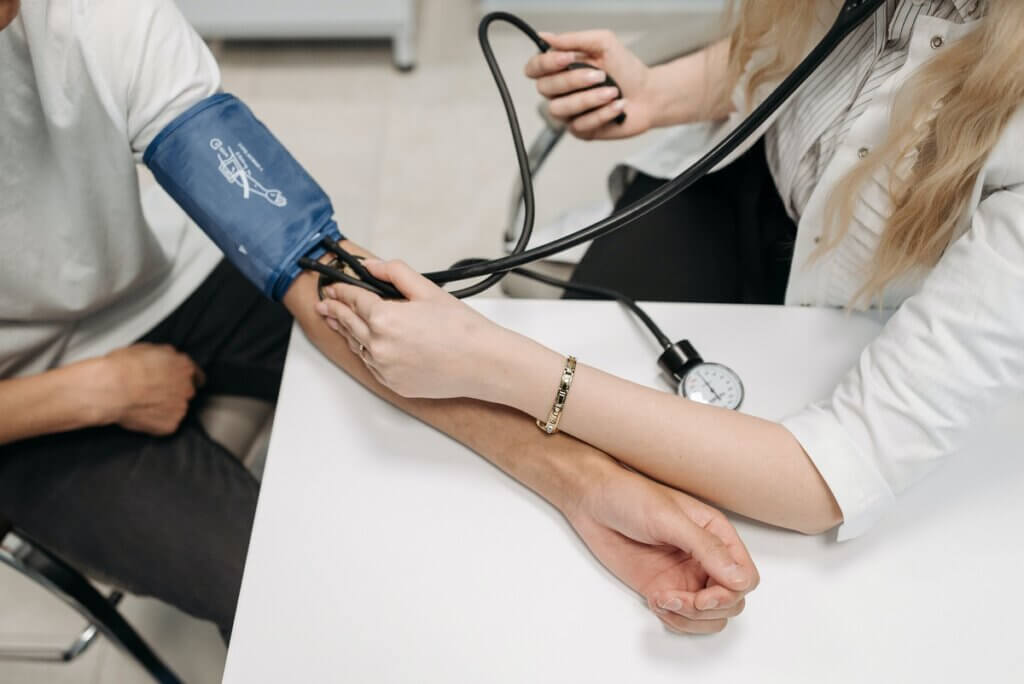
What happens during an allergic reaction?
Allergies are foreign substances, such as food, pollen, dust, mould, or others that cause your body to react, and the immune system triggers protection. When the immune system kicks into gear, it produces antibodies to fend off the foreign substance. Environmental substances such as plants, chemicals, and venom from bugs and insects can all trigger an allergic response in your body.
Most allergies can be split into three forms based on how your body reacts:
- Inhalation
- Contact
- Indigestion
Understanding your allergies
Of you have allergies, you should understand which of these forms causes an allergic reaction for you. The symptoms of the reaction can vary. Some reactions involve simple solutions with an over-the-counter antihistamine, such as a runny nose, sneezing, hives or itchy skin, or feeling nauseous. Many of these reactions are brief and may only last a few minutes.
Hay fever is a common allergic reaction where a person suffers from watery eyes, congestion, sneezing, and sometimes difficulty breathing. With hay fever, these symptoms occur seasonally, usually during warmer months.
More problematic symptoms that indicate a more intense reaction include swelling at the sign of contact or of the eyes, lips, throat, and mouth. Sometimes shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing is other symptoms that you’re having a serious allergic reaction.
What is anaphylaxis?
Anaphylaxis is a severe and life-threatening allergic reaction. The problem with it is that it happens very quickly after exposure or contact with an allergen. It causes your immune system to release chemicals fast and causes your body to go into shock.
When you suffer from anaphylaxis, your blood circulation malfunctions. Your blood pressure drops quickly and air pathways narrow, which increasingly shallows and stops your breathing.
During anaphylaxis your body needs epinephrine. This drug relaxes the muscles within your airways and the tightening of your blood vessels, to allow normal blood circulation to resume. It plays a significant role in increasing your adrenaline to keep your body from going into shock. Many times people who have severe allergies carry around an epinephrine shot to inject in the event of anaphylaxis occurring.
The Immune System’s Response
Histamine is created naturally within the body, so with a normal amount it contributes to everyday functions of your organs, like releasing stomach acid. But, with high amounts during an allergic reaction, it creates a lasting impact on your circulation with side effects that include:
- Increased heart rate (contributing to a drop in blood pressure)
- Expanding blood vessels (can cause you to lose consciousness)
- Muscle contractions (constriction and blocking the breathing)
- Swelling
Even if you’re able to administer the epinephrine or adrenaline shot to someone suffering from a severe allergic reaction, it’s vital to ensure that person is seen by a doctor. Call emergency services (911 in American or 999 in the UK) or take the person to a local hospital for evaluation and monitoring.
How allergies and blood circulation are connected
When allergies impact a person’s breathing, the reaction causes mucus membranes to be inflamed over more extended periods. In many cases, it results in long-term problems, such as asthma or chronic lung disease.
Allergies cause a massive impact on the heart and immune system. Constricted muscles and swelling usually create a lack of blood flow or circulation. Many people get dizzy and faint, some even end up unconscious due to anaphylaxis.
Sometimes people can’t always determine the symptoms they suffer from allergens. It’s a good idea if you have concerns over dealing with some of the common symptoms, like shortness of breath, to ensure it’s not being triggered by allergies.
How to prevent blood circulation problems associated with allergies
Strengthening your heart helps increase blood flow and also aids in improving your body’s oxygen supply. It builds up functions in your organs and can work to decrease the chances of your allergic reactions becoming severe when triggered.
Consider exercise as one of the main methods of helping prevent the harmful implications of an allergic reaction. Exercise is also a proven method to help increase your blood circulation. Exercising daily and keeping your heart rate up can reduce the effects of an allergic reaction on the heart and blood flow.
There are compression socks for nurses and doctors that also ensure an increase in your circulation. If you tend to suffer from cold feet, it can be helpful to wear compression socks to increase the blood flow to your legs. They are designed to apply pressure and maintain blood flow, and reduce discomfort and swelling. It can be welcome if you have allergies, too, since blood circulation plays a large role in increasing your chances of anaphylaxis.
Pay attention to your blood circulation
Even if you don’t suffer from allergies, good circulation is one of the most essential parts of your health. Keeping your blood flow up can increase your body’s immune defenses in the event of coming into contact with an allergen. Antihistamines can also help to block the narrowing of your blood vessels and muscle contractions during an allergic reaction.
The best way to prevent anaphylaxis is by avoiding all contact with allergens. It can be helpful to work with your doctor if you find yourself suffering from allergies to determine the causes and triggers for you to avoid. Have epinephrine and antihistamines handy, and work to keep your blood circulation up to keep those allergic reactions at bay.
Photo from Pexels by Pavel Danilyuk











Leave a Reply